May 2016 Q5 a.
AD Ventures, imports tomato paste from Italy for sale in Ghana. AD Ventures typically buys the tomato paste on open account and pays the euro invoice value two months after receipt of goods. AD Ventures has suffered heavy exchange rate losses of late due to the continuous depreciation of the Ghanaian cedi against the euro. AD Ventures will receive a consignment of tomato paste on 15th May, 2016. The value of this consignment is EUR540,000, which must be settled in two months’ time (settlement deadline being 15th July, 2016).
The current spot exchange rate for the euro is GH¢4.7110/EUR. Financial pundits forecast that the Ghanaian cedi will depreciate against the euro in the coming months. The owner-manager of AD Venture, Akua Donkor, is worried about probable foreign exchange loss her business may suffer when the invoice value is settled in two months’ time.
Akua Donkor has heard of the possibility of hedging AD Ventures’ currency exposure with a forward contract or futures contract but does not know what these contracts are. She has asked you to advise her on what to do to hedge against the underlying exposure relating to the EUR540,000 tomato paste consignment.
You would like to recommend a futures market hedge to Akua Donkor. You searched the derivatives market; and you found a futures contract on the euro that matures in August 2016. Other relevant details of the contract follow:
Contract size EUR100,000
Futures contract price GH¢4.8112/EUR
Required:
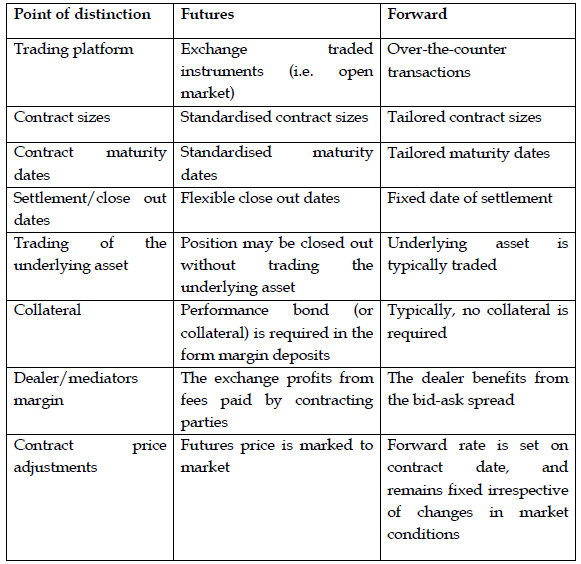
i) Explain to Akua Donkor FOUR differences between a forward contract and a futures contract. (4 marks)
View Solution
ii) Currency risk exposure may be transaction risk, economic risk, or translation risk. Which of the three kinds of currency risk exposure is AD Ventures facing in relation to the EUR540,000 tomato paste consignment. Explain why. (4 marks)
View Solution
A firm that engages in international business transactions faces transaction risk when it has contractual cash flows that are fixed in the foreign currency and the exchange rate might change over the contract period. For instance, transaction risk exists when value of imports and exports are fixed in the foreign currency and there is movement in the exchange rate between the invoice date and settlement date.
Translation risk is when an organisation will suffer exchange losses when the results of its foreign branches and subsidiaries are translated into the home currency.
Economic risk refers to the effect of exchange rate movement on the international competitiveness of an organisation. It refers to the present value of longer-term cash flows. It exists when an organisation faces competition from domestic producers/traders in the foreign country or local importers in the home country.
Analysis of AD Ventures case:
By engaging in the import transaction that will be settled in the future, AD Ventures faces contractual cash flow (here the obligation to pay EUR540,000). Moreover, the contractual cash flow is fixed in the foreign currency, the euro.
Conclusion on risk type:
With respect to the tomato import from Italy, AD Ventures is facing transaction exposure to currency risk.
iii) Explain to Akua Donkor, THREE disadvantages of hedging the euro exposure with futures hedge. (6 marks)
View Solution
- Contract size cannot be tailored to the exact requirements the investor. This means that the investor’s underlying exposure may not be covered effectively, resulting in hedge inefficiency.
- Contract maturity date cannot be tailored to synchronise with maturity date of underlying exposure. For instance, AD Ventures’ euro obligation falls due in January 2016 but the available contract matures in February 2016. This results in hedge inefficiency.
- Basis risk is inherent in futures hedge. There is the risk that the futures price may move by a different amount from the price of the underlying asset.
- Unlike options, the investor has an obligation to either trade the underlying asset or take an opposite position to close out. This means that the investor does not have the flexibility to take advantage of favourable price movements in the spot market.
- Unlike forwards, futures requires opening and maintenance of a margin account which involves deposit of cash or cash equivalent.