Zed Ltd is considering the immediate purchase of some, or all, of the share capital of one of two firms-Fasco Ltd and Boscan Ltd. Both Fasco Ltd and Boscan Ltd have one million ordinary shares issued and neither company has any debt capital outstanding
Both firms are expected to pay a dividend in one year’s time-Fasco expected dividend amounting to 30p per share and Boscan’s being 27p per share. Dividends will be paid annually and are expected to increase over time. Fasco’s dividends are expected to display perpetual growth at a compound rate of 6% per annum. Boscan’s dividend will grow at the high annual compound rate of 33⅓% until a dividend of 64p per share is reached in year 4. Thereafter Boscan’s dividend will remain constant.
If Zed is able to purchase all the equity capital of either firm then the reduced competition would enable Zed to save some advertising and administrative costs which would amount to
GH¢225,000 per annum indefinitely and, in year 2, to sell some office space for GH¢800,000. These benefits and savings will only occur if a complete takeover were to be carried out. Zed would change some operations of any company completely taken over, the details are:
- Fasco – No dividend would be paid until year 3. Year 3 dividend would be 25p per share and dividends would then grow at 10% per annum indefinitely.
- Boscan – No change in total dividends in years 1 to 4, but after year 4 dividend growth would be 25% per annum compound until year 7. Thereafter annual dividends would remain constant at the year 7 amount per share.
An appropriate discount rate for the risk inherent in all the cash flows mentioned is 15%
Required:
a) Calculate the valuation per share for a minority investment in each of the firms, Fasco and Boscan, which would provide the investor with a 15% rate of return. (6 marks)
View Solution
Using the dividend valuation model the value of ordinary shares is given by:
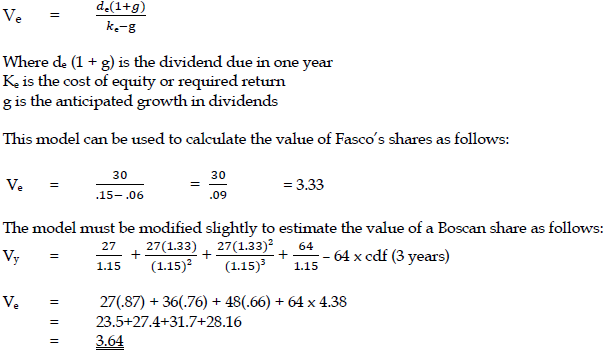
b) Calculate the maximum amount per share which Zed should consider paying for each company in the event of a complete takeover. (8 marks)
View Solution
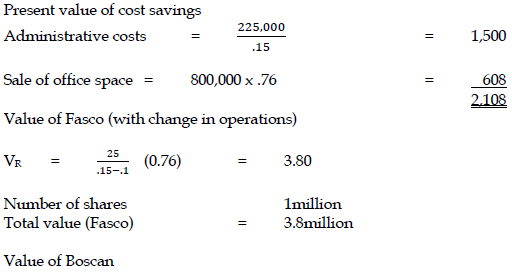
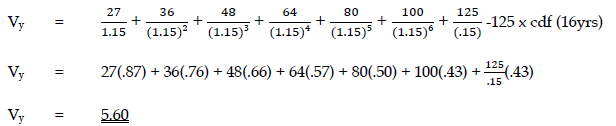
c) Comment on any limitation of the approach used in part (a) and specify the other major factors which would be important to consider if the proposed valuations were being undertaken as a practical exercise. (6 marks)
View Solution
- The calculations in part (a) are based on the dividend valuation model which depends on the belief that share prices are the discounted present value of the future dividend stream. There are strong theoretical justifications for this model in the context of a perfect capital market. However, in a less than perfect market the failure of the model to take any account of short run earnings (i.e. accounting profits) or underlying asset values, may limit its usefulness. There are further practical problems in applying the model which relates to determining the values of the constituent variables. Of these ‘g’ the anticipated growth rate and Ke, the cost of capital or required return, present particular problems. ‘g’ the anticipated future dividend growth. It is usually estimated by extrapolating past growth or by using the Gordon Growth Model. Whichever approach is taken the resulting estimate is inevitably suspect.
- Selecting an appropriate discount rate to convert future cash flows to a capital value also present special difficulty. Generally the appropriate rate reflects the risk-free rate and a premium for risk suitable for the share being valued. It is obviously difficult to determine such a rate. In this question the required return is given as 15%. This is used for both Red and Yellow and for all time periods. This in turn assumes that the risks associated with both companies over all relevant time periods are identical. This seems unlikely, particularly in view of the differences in growth rates for Red and Yellow. It would be more usual to assume that the very high growth in Yellow’s dividends during the first four years would result in riskier cash flows.
- Further practical difficulties would include the management organization of the post-merger company, competitive response and arranging the finance for the takeover.
- Finally, in transactions of this type there are inevitably tax consequences that would have to be carefully considered.
