JB Investments Holding Ltd (JB) is a multinational company that is committed to a policy of expansion into African countries. JB finances foreign projects with loans obtained in the currency in which project cash flows are received. JB financed an operation in Liberia with a syndicated loan of $20 million. Currently, the loan has three years to maturity. The loan requires semiannual interest payments at a fixed rate of 6.5% per annum, but JB prefers a floating interest rate as the pattern of cash flows from the Liberian project has changed.
The Finance Director talked to the creditors about JB’s preference for a floating interest rate. The creditors have agreed to accept a floating rate of LIBOR plus 200 basis points over the remaining three years of the loan term. However, the Finance Director feels that this rate is rather too high considering JB’s credit rating. She is therefore considering two alternatives for managing the interest rate risk exposure.
Alternative 1: Coupon swap with a bank
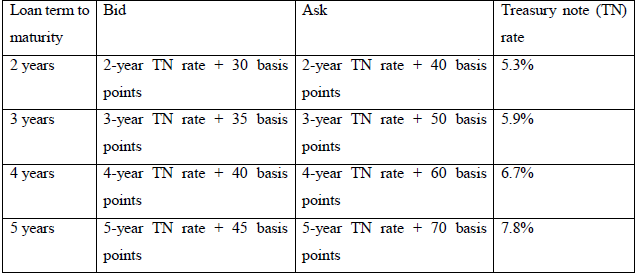
Engage in a coupon swap with UT Bank through which JB trades-in its fixed rate interest payments obligation for floating rate interest payments. The table below presents UT Bank’s bid and ask quotes for fixed dollar coupon rates:
Floating rate quotation:
- Floating rates are pegged at 6-month dollar LIBOR plus 100 basis points.
Alternative 2: Coupon swap with another multinational company
Engage in a coupon swap with McEwen Ltd, a multinational company that has a floating rate dollar debt but prefers fixed coupon payments. The interest rate on McEwen’s dollar debt is LIBOR plus 150 basis points but it can borrow fixed rate dollars at 8%. Assume JB can borrow floating rate dollars at LIBOR plus 200 basis points.
The Board of Directors of JB Investments Holdings Ltd are considering a transfer pricing policy for transfer of goods and services amongst the company and its foreign subsidiaries.
Required:
Explain THREE (3) internal factors (motivations) for transfer pricing, which the board should consider in formulating a transfer pricing policy for the company. (6 marks)
View Solution
- Performance evaluation: In the case where units within the multinational are treated as autonomous profit centres, transfer pricing is needed to evaluate the performance of each unit effectively. Without transfer pricing, performance of selling departments may be underrated and that of buying departments may be overrated, or otherwise.
- Management incentives: An effective transfer pricing system that rewards managerial efficiency and exposes efficiencies will serve as incentive for good performance.
- Cost allocation: If there are units within the JB group that are treated as cost centres, an effective transfer pricing system will allow them to charge for their services to the group and thus permit them to recover their costs and perhaps record a mark-up. This will boost morale of managers at cost centres, and encourage economy and efficiency with the use of their services amongst units in the group.
- Financing consideration: Transfer pricing can be used to provide financing to a subsidiary by the parent company undercharging the subsidiary for goods and services transferred.
