The Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA) defines Internal Auditing as:
“An independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization’s operations. It helps an organization to accomplish its objectives by bringing a systematic, disciplined approach to evaluate and improve the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes”.
Required:
Assess the importance of THREE recommendations the IIA has made to ensure that internal auditors remain independent even though they are employees of the company. (4 marks)
View Solution
One of the most important aspects of IA is to ensure that Internal Auditors remain independent of the functions they audit. To ensure this the IIA makes many recommendations especially for IA since the staff in the IA function are also employees of the same organization they audit.
To promote the independence of IA the IIA makes the following recommendations:
- The IIA recommends that the Chief Audit Executive or the Head of Internal Audit must be appointed and can only be dismissed by the Audit Committee, a sub-committee of the Board of Directors charged with oversight responsibly for all Audit related matters and not by the management of the organization.
- IA reports administratively to the CEO of the organization but functionally (that in its reporting duties) to Audit Committee.
- The IIA also recommends that IA must occupy a position in the Organisational Structure that ensures that the CAE is next to the Board of Directors and above all others on the organization, as shown below:
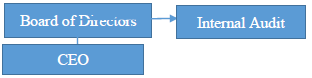
- The IIA also recommends that internal audit activities shall remain free of influence by any element in the organization, including matters of audit selection, scope, procedures, frequency, timing, or report content; and
- Internal Auditors shall have no direct operational responsibility or authority over any of the activities in the organisation. Accordingly, they shall not develop or install systems or procedures, prepare records, or engage in any other activity which would normally be audited (this is to avoid self-review) and so remain independent of all operational issues in the organisation.
