a) Explain what is meant by basic standards and ideal standards and their effect on employee motivation. (5 marks)
View Solution
An ideal standard is one which can be attained under perfect operating conditions: no wastage, no inefficiencies, no idle time, and no breakdowns.
A basic standard is a standard which remains unchanged over the years and is used to show trends.
Effect on employee motivation:
- Ideal standards can be seen as long-term targets but are not very useful for day-to-day control purposes as they cannot be achieved. It is claimed that they provide employees with an incentive to be more efficient.However, they may have an unfavourable effect on employee motivation as variances will always be adverse.
- Basic standards may have an unfavourable effect on motivation as employees discover over time that they are easily able to achieve the standards.
b) Sasraku Ltd manufactures and sells standard quality fuel pumps. Other companies integrate these pumps in their production of petrol engines. At present, Sasraku Ltd manufactures only three different types of fuel pumps-oil pump, gas pump and diesel pump. Simon, the Management Accountant, allocates fixed overheads to these pumps on an absorption costing system.
The standard selling price, volumes and cost data for these three products for the last period are as follows:
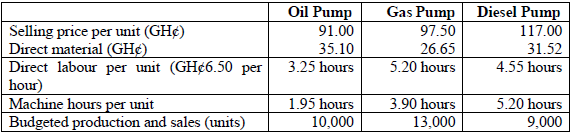
The total fixed production overhead for the last period was estimated in the budget to be GH¢526,500. This was absorbed on a machine hour basis.
The Board of Directors has decided to calculate the variances for the period in order to analyse the sales performance of the company.
The following information of actual volumes and selling prices for the three products in the last period was obtained.
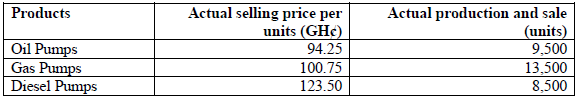
Required:
i) Calculate standard profit per unit (3 marks)
View Solution
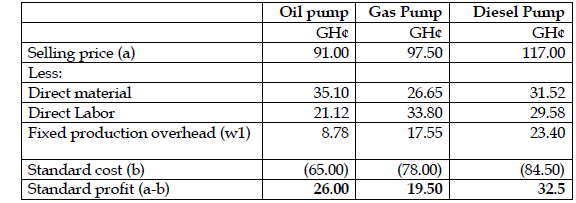
Working:
W1: calculation of overhead absorption rate
Budget machine hours = (10,000*1.95) + (13,000*3.90) + (9,000*5.20) =117,000 hours
As company follows absorption costing method, fixed overheads are allocated on machine hours’ basis.
Overhead adsorption rate = GH¢526,500/117,000 hours = GH¢4.50 per machine hour.
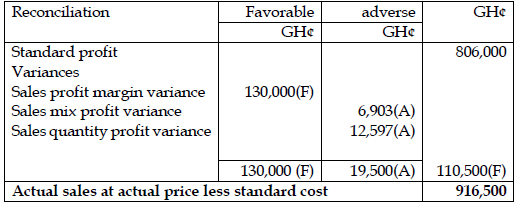
ii) Calculate the following variances for overall sales for the last period: (8 marks)
- Sales profit margin variance
View Solution
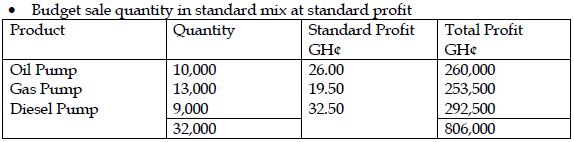
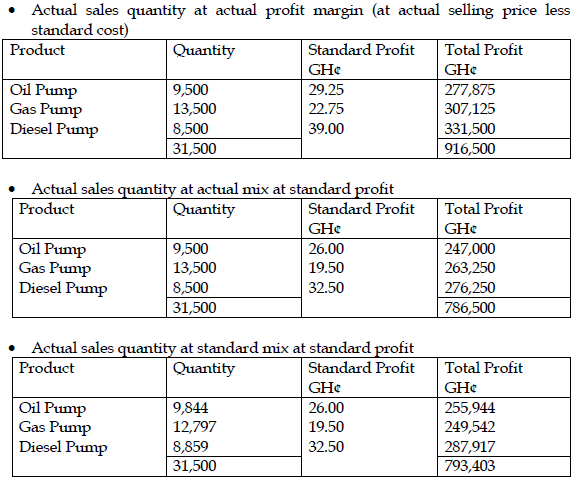
Alternative approach to actual sales quantity in standard mix at standard profit
= Actual quantity * average standard profit per unit
=31,500 units* GH¢25.1875 per units
= GH¢793,403
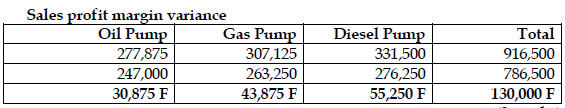
ALTERNATIVE SOLUTION:
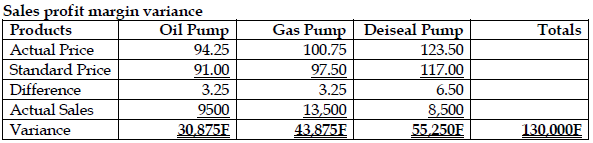
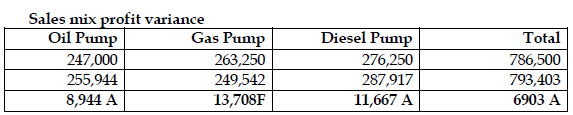
- Sales mix profit variance
View Solution

Alternative approach to actual sales quantity in standard mix at standard profit
= Actual quantity * average standard profit per unit
=31,500 units* GH¢25.1875 per units
= GH¢793,403
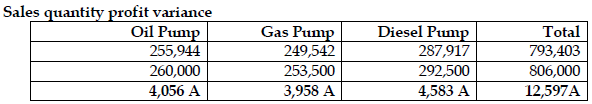
- Sales quantity profit variance
View Solution

Alternative approach to actual sales quantity in standard mix at standard profit
= Actual quantity * average standard profit per unit
=31,500 units* GH¢25.1875 per units
= GH¢793,403
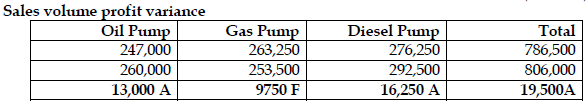
- Sale volume profit margin
View Solution

Alternative approach to actual sales quantity in standard mix at standard profit
= Actual quantity * average standard profit per unit
=31,500 units* GH¢25.1875 per units
= GH¢793,403
iii) Prepare a statement showing the reconciliation of budgeted profit for the period to actual sales less standard cost. (4 marks)
View Solution