The following is a summary of the Financial Statements of two companies in the retailing business.
Required: (10 marks)
a) Calculate the following ratios for each company:
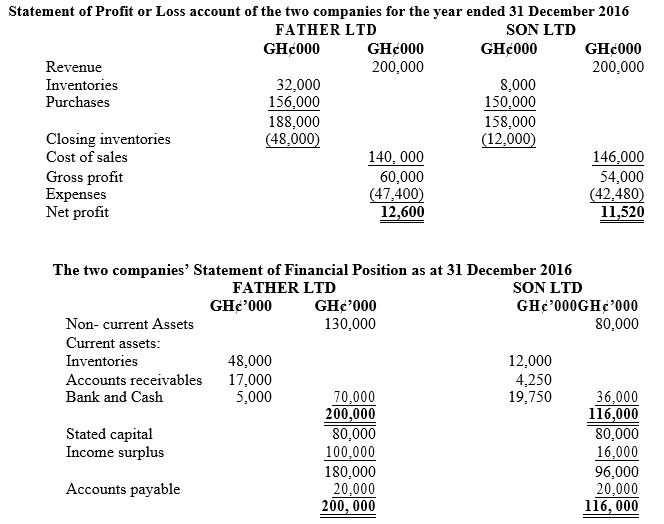
i) Current ratio
View Solution
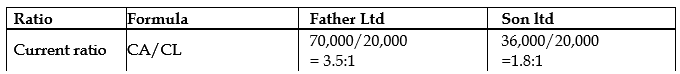
ii) Acid Test ratio
View Solution
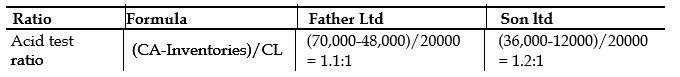
iii) Gross profit margin
View Solution
iv) Return on capital employed
View Solution
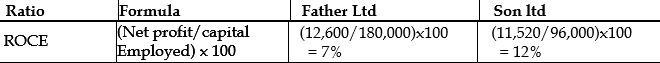
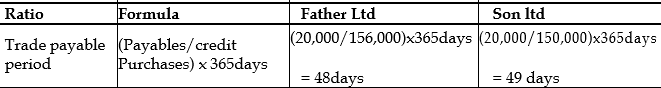
v) Trade Payable period
View Solution
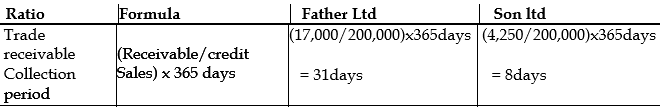
vi) Receivable collection period
View Solution
b) Using the information in (a) above, interprete the results of the ratios under three broad categories of profitability, liquidity and efficiency. (10 marks)
View Solution
Liquidity:
Liquidity is the ability of an entity to be able to pay for its short term obligations as and when they fall due without any difficulties. Again, this payment should not affect the working capital of the firm and as a result the company continues to operate without any operational difficulties. Applying this understanding to both Father and Son limited above suggest that the current assets of Father limited can pay for its current liabilities about 3.5 times as opposed to 1.8 times of Sons limited. However, adjusting for inventories the quick ratios of both companies shows 1.1:1 and 1.2:1 respectively for Father and Son. This suggests that inventories forms a significant part of the current assets of Father limited and may not be convertible into cash very quickly. The quick ratio indicates that slightly Son limited is better off with respect to its liquidity position. At the moment both companies can meet their current short-term obligations but Father Limited may have difficulty going forward with its significant nature of inventories.
Profitability:
Every business wants to make the highest profit possible for its shareholders but care needs to be taken that profit is not equal to cash.
Looking at the gross margin of both Father and Son Limited, the gross margin is 30% and 27% respectively with the same level of sales. Better management of cost of sales may be key to the differences in the margins as depicted by the calculations above. This may also be partly due to the credit policies of both companies. On the face value it may not be fair to say that Father limited is doing well because it has 3% more than that of Sons Limited. Return on capital employed really looks at the efficiency in the utilization of capital in earning or generating profit in percentage terms. The higher this ratio the better management would have better utilize capital invested by shareholders and vice versa. Father Limited from that calculation has return on capital of 7% compared with 12% of Sons Limited. This suggests that Sons Limited is better using every pesewa invested by its shareholders efficiently and effectively as opposed to Father Limited. Father limited may need to change this situation as a matter of urgency.
Efficiency:
Activity or efficiency ratios assesses how efficient and effective an entity is with respect to its credit policies as well as general operational decision making processes. The receivable collection period indicate the time period it takes for management of an entity to be able to collect its debts from credit customers or debtors. Generally, the shorter time it takes the entity to do that the better since this will enhance the liquidity position of the entity. Looking at the ratios above Son Limited collect its debts within 8 days as opposed 31days for Father limited. This suggests that a huge amount of sale of Father Limited is on credit. This cannot be said of Son Limited as significant amount of its sales appears to be in cash sales and therefore it is not surprising that it is slightly better off with respect to its liquidity position. Similarly, trade payable period is the time an entity uses to settle its suppliers. A better supplier relationship could allow for a longer period for payment and this is a very good source of finance to the entity. Both companies seem to have relatively the same period of 48days and 49days for Father and Son Limited respectively.
