Nov 2015 Q2
ABC Manufacturing Ltd (ABC) is an indigenous Ghanaian company that manufactures components used in air conditioners. The company now wants to manufacture air conditioners for sale in Ghana. Though the manufacture of air conditioners will be a completely new business, directors of ABC plan to integrate it into the company’s core business.
ABC has premises it considers suitable for the project. This premises was acquired two years ago at the cost of GHS50,000. ABC will acquire and install the needed machinery immediately, so production and sales can commence during the first year. The directors of ABC intends to develop the project for five years and then sell it to a suitable investor for an after-tax consideration of GHS20 million.
The following data are available for the project:
1. The cost of acquiring and installing plant and machinery needed for the project will be GHS5 million at the start of the first year. Tax-allowable depreciation is available on the plant and machinery at the rate of 30% on reducing balance basis.
2. Working capital requirement for each year is equal to 10% of the year’s anticipated sales. ABC has to make working capital available at the beginning of the respective year. It is expected that 40% of working capital will be redeployed to other projects at the end of the fifth year when the project is sold.
3. It is expected that 2,000 units will be manufactured and sold in the first year. Unit sales will grow by 5% each year thereafter.
4. Unit sales price is estimated at GHS2,200 in the first year. Thereafter, the unit sales price is expected to be increased by 10% each year.
5. Unit variable cost will be GHS1,100 per unit in the first year. Unit variable cost is expected to increase by 8% each year after the first year.
6. Fixed overhead costs are estimated at GHS1·5 million in total in each year of production/sale. One-half of the total fixed overhead costs are head office allocated overheads. After the first year of production/sales, fixed overhead costs are expected to increase by 5% per year.
ABC Ltd’s pays tax at 25% on taxable profits. Tax is payable in the same year the profit is earned.
ABC Ltd uses 25% as its discount rate for new projects but the directors feels that this rate may not be appropriate for this new venture.
Currently, ABC can borrow at 500 basis points above the five-year Treasury note yield rate. Ghana’s government is enthused by the venture and has offered ABC a subsidised loan of up to 60% of the investment funds required at an interest rate of 200 basis points above the five-year Treasury note yield rate. ABC plans to use debt capital to finance the project by taking advantage of the government’s subsidised loan and raising the balance through a fresh issue of 5-year debentures. Issues costs, which can be assumed to be tax-deductible expenses, will be 5% of the gross proceeds from the debenture offer. The financing strategy for the project is not expected to affect the company’s borrowing capacity in any way.
ABC Ltd will be the first indigenous Ghanaian company to manufacture air conditioners in Ghana. However, it will be competing with XYZ Ltd, a listed company with majority shares held by foreign investors. The cost of equity of XYZ Ltd is estimated to be 20% and it pays tax at 22%. XYZ has 10 million shares in issue that are trading at GHS5.5 each, and bonds with total market value of GHS40 million.
The five-year Treasury note yield rate is currently 10% and the return on the market portfolio is 18%.
Required:
Evaluate, on financial grounds, whether ABC should implement the project or not. (20 marks)
View Solution
The project presents different business risk (as it involves a new business venture) and increases financial risk (as its financing method will increase the company’s gearing). In addition, there are associated financing side effects that need to be factored into the financial appraisal. Adjusted present value (APV) will be a more efficient appraisal method than the traditional NPV
approach. (Follow the 3 steps below)
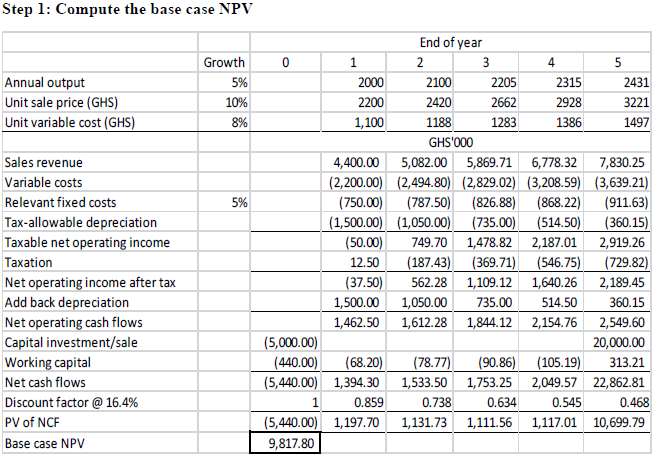
WORKINGS:
1. Tax-allowable depreciation
![]()
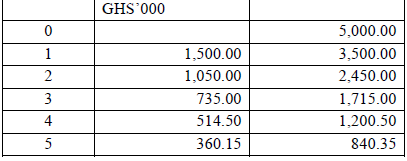
2. Cost of equity as if company is ungeared
As the new project is a completely new business, an appropriate cost of equity is one that reflects the level of business risk associated with the new business. This can be derived from that of the competitor, XYZ as under:
Using MM Proposition II with tax:
![]()
XYZ’s cost of equity, ke(g) = 20%
Market value of XYZ’s equity = 10m x GHS5.5 = GHS55m
Market value of XYZ’s debt = GHS40m
XYZ’s tax rate, t = 22%
Cost of debt, kd = 10% (taken to be the treasury note rate)
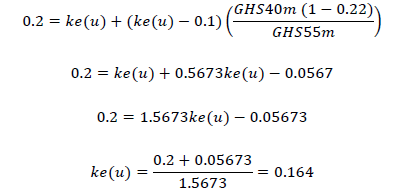
Alternatively, obtain asset beta of XYZ and put that into the capital asset pricing model to obtain ungeared cost of equity as under:
Equity beta of XYZ is 1.25:
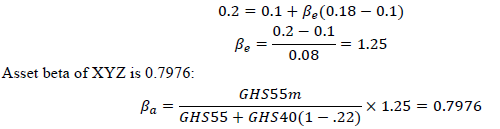
According to CAPM, the ungeared cost of equity is 16.38%:
𝑘𝑒(𝑢)=0.1+0.7976(0.18−0.1)=0.164
Note: The ungeared cost of equity may be assumed 16% so as to read present value interest factors from the interest factor tables.
Step 2: Calculate PV of financing side effects
Financing side effects that apply in this case are –
- the issue cost and its associated tax shield
- annual interest payments on debt financing
- benefit from subsidized loan from the government
Necessary adjustments for the financing side effects follow.
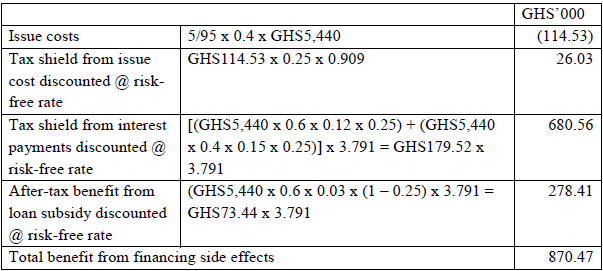
Notes:
- The issue costs may be included in funds borrowed instead.
- The calculation above assumes that the entire issue costs will be expensed in the first year. One may choose to amortize it over the 5-year forecast period and discount the annual tax shields accordingly.
- PV of tax shield and subsidy benefit are based on the 5-year government debt yield rate. It may be discounted at the company’s cost of debt, 15% (5-year yield rate plus 500 basis points) on the grounds that the benefits will accrue to the company only when it is able to discharge its financial obligation and 15% reflects the credit risk of the company.
Step 3: Compute APV by adjusting base case NPV for financing side effects

Conclusion:
As the APV is positive, the value of ABC will increase if the proposed project is implemented.

