Nov 2020 Q2 b.
Following the government’s commitment to build one factory in each district in Ghana and its desire to ensure food sufficiency through the planting for food and job program, an investor from Singapore intends to invest in shoe manufacturing company to be located at Accra in the Greater Accra Region of Ghana. He also considers starting a juice manufacturing company at Nsawam in the Eastern Region of Ghana in response to the investment drive of the government.
As part of the investment, he intends to incur the following cost and start operations in 2018 on either proposal, which is the Shoe manufacturing company or the Juice manufacturing company.
GH¢
Building 7,200,000
Plant and Machinery 11,700,000
Furniture and Fittings 180,000
Computers 180,000
Additionally, he intends to recruit fresh graduates from the All Nations University College of Ghana.
It is further projected that in the first three years, that is 2018, 2019 and 2020, it will incur GH¢36,000, GH¢32,400 and GH¢18,000 losses respectively.
The investor hopes to start making profit from the year 2021. He intends to borrow at 20% interest from his USA associate amounting to the equivalent of GH¢100,000,000. The equity he intends to start with is GH¢36,000,000.
Required:
As a tax adviser, evaluate the proposed investment by the Singaporean investor and the tax implication on the various activities highlighted in the scenario. (10 marks)
View Solution
The proposed investment will help in the following:
Tax Rebate
Investment in the shoe manufacturing in Accra will create for the entity a tax payment at the rate of 25%
On the other hand, Juice manufacturing in Nsawam will create a tax paying responsibility at the rate of 12.50 % with a rebate of 50% from the corporate tax at the rate of 25% based on the location. (2 marks)
Locational Incentive
Accra /Tema corporate tax rate is 25%
Regional capitals tax payable is at the rate of 18.75% with a rebate of 25%
Any other area 12.50% with a rebate of 50% (1 mark)
Capital allowance
The cost it intends to incur in the following depreciable assets shall rank for capital allowance for the entity.
GH¢
Building 7,200,000
Plant and Machinery 11,700,000
Furniture and fittings 180,000
Computers 180,000
The above constitute depreciable assets and shall be granted capital allowance:
Building falls under pool 4 and shall be granted capital allowance at the rate of 10% straight line method.
Plant and Machinery fall under pool 2 which will be granted capital allowance at the rate of 30% reducing balance method.
Furniture and fittings shall fall under pool 3 and be granted capital allowance at the rate of 20% reducing balance method
Computer falls under pool 1 and capital allowance at the rate of 40% on reducing balance method.
The essence of capital allowance is to reduce the chargeable income and consequent tax payable. (3 marks)
Fresh graduate incentive
The recruitment of fresh graduates will also generate benefit to the entity as follows:
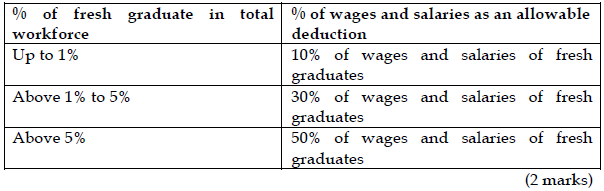
Loss carry forward
The losses projected to be incurred as follows
2018 36,000
2019 32,400
2020 18,000
The above losses shall be carried forward for 5 years and shall be deducted in the order in which they occur. Each year’s loss shall be carried forward for five years against income in line with section 17 of Act 2015 (Act896). (1 mark)
Thin capitalization Issues
The borrowing of 100,000,000 against equity of 36,000,000, has no tax implication. The safe harbour rule is Debt equity ratio of 3: 1.
Equity of 3 time is GH¢108,000,000 (3*36,000,000), which is higher than the amount of loan to be secured from a related party. The interest on the loan shall all be allowable deduction to the extent that the interest is at a commercial rate.
If the debt equity ratio is more than 3: 1, the interest on the excess of the loan above 3:1 ratio shall be disallowed for tax purpose. (1 mark)