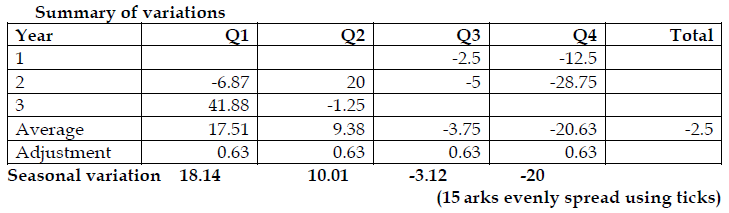
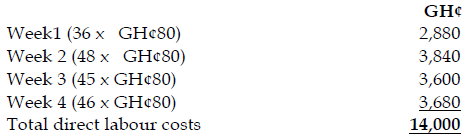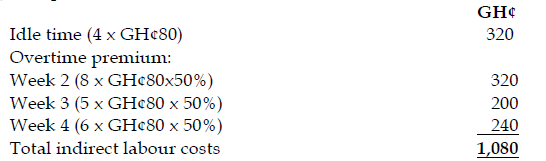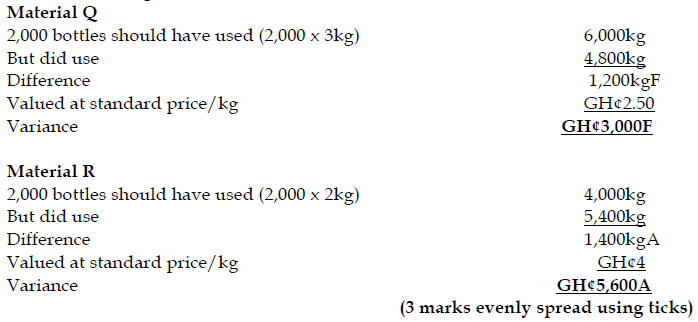May 2019 Q1 b.
The money market is the arena in which financial institutions make available to a broad range of borrowers and investors the opportunity to buy and sell various forms of short-term securities. The short-term debts and securities sold on the money markets which are known as money market instruments have maturities ranging from one day to one year and are extremely liquid.
Required:
Explain the following short term market instruments:
i) Bankers’ acceptance (2 marks)
View Solution
A banker’s acceptance is an instruments produced by a nonfinancial corporation but in the name of a bank. It is document indicating that such-and-such bank shall pay the face amount of the instrument at some future time. The bank accepts this instrument, in effect acting as a guarantor. To be sure the bank does so because it considers the writer to be credit-worthy. Bankers’ acceptances are generally used to finance foreign trade, although they also arise when companies purchase goods on credit or need to finance inventory. The maturity of acceptances ranges from one to six months.
ii) Commercial Paper (2 marks)
View Solution
Commercial paper refers to unsecured short-term promissory notes issued by financial and nonfinancial corporations. Commercial paper has maturities of up to 270 days (the maximum allowed without SEC registration requirement). Dollar volume for commercial paper exceeds the amount of any money market instrument other than T-bills. It is typically issued by large, credit-worthy corporations with unused lines of bank credit and therefore carries low default risk.
Unlike some other types of money-market instruments, in which banks act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, commercial paper is issued directly by well-established companies, as well as by financial institutions. Banks may act as agents in the transaction, but they assume no principal position and are in no way obligated with respect to repayment of the commercial paper. Companies may also sell commercial paper through dealers who charge a fee and arrange for the transfer of the funds from the lender to the borrower.
iii) Repurchase Agreement (Repo) (2 marks)
View Solution
Repurchase agreements—also known as repos or buybacks—are Treasury securities that are purchased from a dealer with the agreement that they will be sold back at a future date for a higher price. These agreements are the most liquid of all money market investments, ranging from 24 hours to several months. In fact, they are very similar to bank deposit accounts, and many corporations arrange for their banks to transfer excess cash to such funds automatically.
iv) Term deposit (2 marks)
View Solution
A term deposit is a cash investment held at a financial institution. Your money is invested for an agreed rate of interest over a fixed amount of time, or term. Term deposits can be invested into a bank, building society or credit union. When the money is deposited, the customer understands that the money is there for the pre-determined period which usually ranges from 1 month to 5 years and the interest rate is guaranteed not to change for that nominated period of time. Typically, the money can only be withdrawn at the end of the period – or earlier with a penalty attached.
Term deposits are popular with investors who prefer capital security and a set return as opposed to the fluctuations of, say, the share market. Many investors also use term deposits as a part of their investment mix.