a) ISA: 500 Audit evidence requires the auditor to obtain sufficient, appropriate evidence to be able to draw reasonable conclusions on which to base the audit opinion. That evidence should be relevant to the financial statements assertions.
Required:
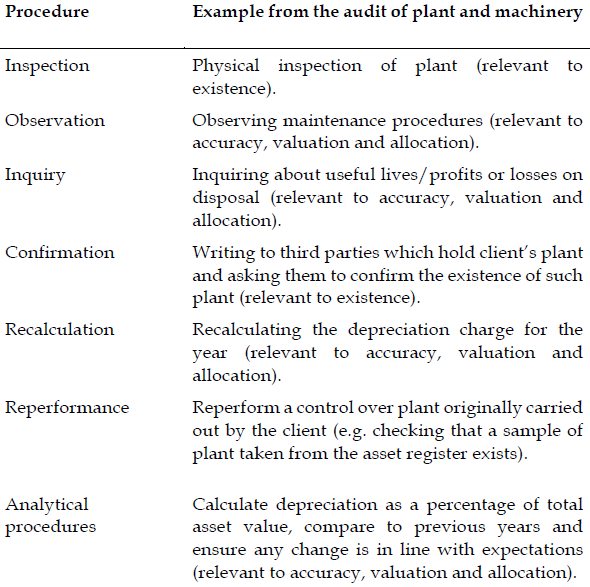
ii) Identify FIVE (5) of the seven main audit testing procedures (for example inspection) and give an example of how each might be used in the audit of plant and machinery. State the assertion that is being tested in each case. (5 marks)
View Solution
b) Tamale Pharma specialises in the development of drugs for the pharmaceutical industry.
Required:
State how you could verify the following items appearing in the statement of financial position of Tamale Pharma as at 31 December 2018. You are not required to consider presentation and disclosure: (7 marks)
i) Patents.
View Solution
- A register should be maintained giving a description of each patent, its cost, depreciation and net book value. Test a sample of the patents from the register against patent documents.
- Ensure patent documents are stored in a secure place.
- Vouch additions in the year (or a sample) to purchase documentation, including authorisation in the board minutes, or evidence of approval by a senior company official. If the patent originates from the company itself, vouch to filing documentation.
- Agree costs of the company’s own patents to the documentation supporting the direct costs of application. All other related costs should be treated as research and development.
- Ensure that patents are written off over their useful lives, and that the rates used are reasonable.
- Check (a sample of) the amortisation calculations.
- Consider whether the useful lives being used are reasonable.
- Consider whether there are any business circumstances which might necessitate the need for an impairment write off.
- Ensure any impairment has been correctly dealt with.
(3 points for 3 marks)
ii) Research and development.
View Solution
Examine supporting documentation (e.g. invoices, timesheets) to ensure that any amounts capitalised are development costs, and comply with the strict criteria laid down in IAS 38 i.e.
- probable economic benefits
- intention to complete the asset and use or sell it
- resources exist to complete the project
- ability to use or sell the asset
- technical feasibility of completing the asset
- expenditure can be measured reliably.
To verify these costs, consider:
- project evaluation reports
- whether an independent assessor should be consulted if the information is of a highly technical nature
- ensure that any non-current assets used for the purposes of research and development have been capitalised and depreciated as required by IAS 16.
